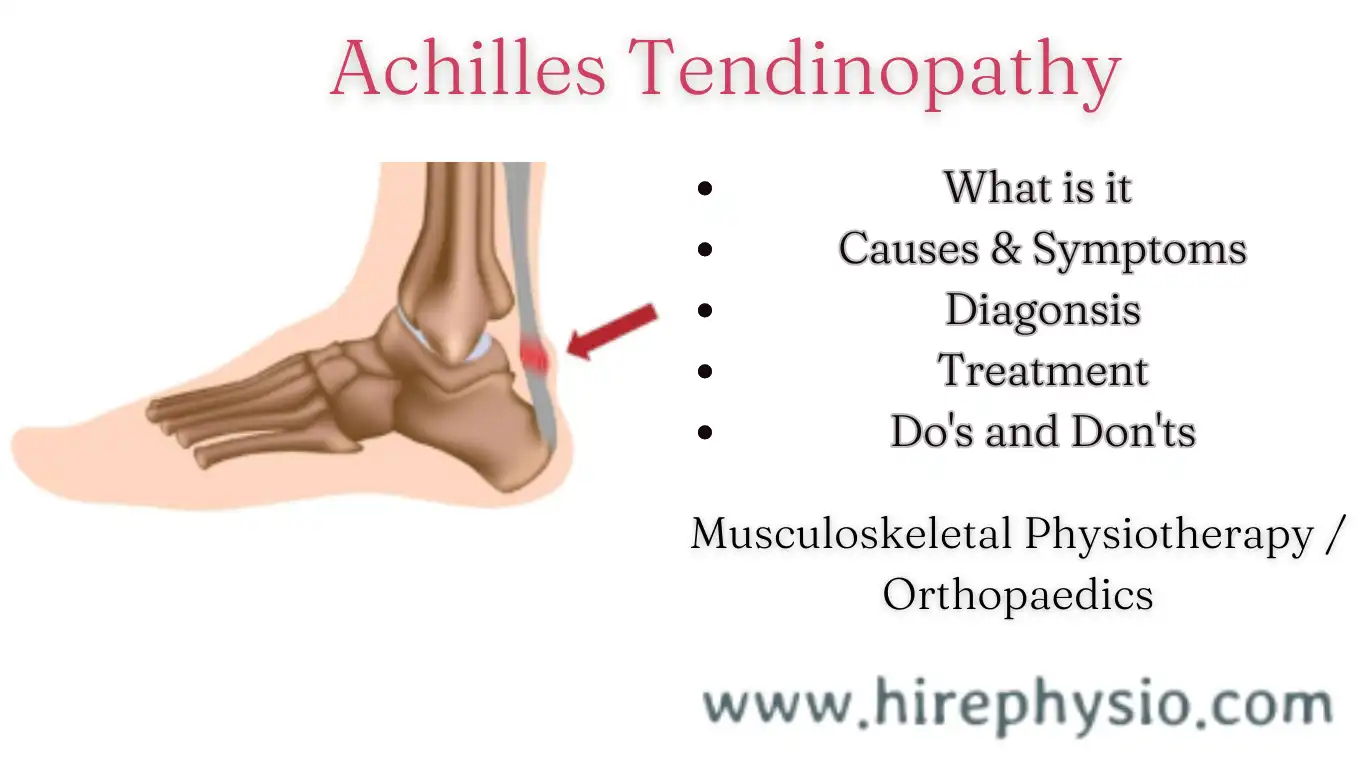
WHAT IS ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
Achilles tendinopathy is a common condition that affects the Achilles tendon, the thick band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This condition can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the back of the ankle, and can limit the ability to walk, run or participate in physical activities. If you’re experiencing symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy, it’s important to seek the help of a qualified physiotherapist who can provide a personalized treatment plan to help you recover. At Hirephysio.com, we make it easy to find a physiotherapist near you who can help you manage your Achilles tendinopathy and get back to doing the things you love.

Effective Treatment Options for ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY) : Get Quick Relief Now! || Hirephysio.com
WHO GETS ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
Achilles tendinopathy is a condition that affects the Achilles tendon, the thick band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It can occur in anyone who puts repeated or excessive stress on the Achilles tendon, but some people are more at risk than others.
Here are some factors that can increase the risk of developing Achilles tendinopathy:
- Age: The risk of Achilles tendinopathy increases with age, as the tendon becomes less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Physical activity: Athletes and people who engage in activities that involve repetitive jumping or running, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, are more likely to develop Achilles tendinopathy.
- Foot structure: People with flat feet or high arches may be more prone to developing Achilles tendinopathy due to the altered biomechanics of the foot.
- Tight calf muscles: Tight calf muscles can put extra stress on the Achilles tendon, increasing the risk of tendinopathy.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can put extra stress on the Achilles tendon, increasing the risk of tendinopathy.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can weaken the Achilles tendon and increase the risk of tendinopathy.
It’s important to note that anyone can develop Achilles tendinopathy, even if they don’t have any of the risk factors listed above.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
Achilles tendinopathy can be caused by several factors, including:
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon can cause microtrauma and lead to tendinopathy. This can be due to activities such as running, jumping, or dancing.
- Inadequate warm-up or cool-down: Not properly warming up before exercise or cooling down after can put added stress on the Achilles tendon, increasing the risk of tendinopathy.
- Poor foot mechanics: Poor foot mechanics, such as flat feet or high arches, can cause abnormal forces to be applied to the Achilles tendon, leading to tendinopathy.
- Tight calf muscles: Tight calf muscles can put extra strain on the Achilles tendon and lead to tendinopathy.
- Age-related degeneration: As we age, the blood supply to the Achilles tendon decreases, making it more prone to injury.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can weaken the Achilles tendon and increase the risk of tendinopathy.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can increase the risk of tendinopathy.
- Trauma: A direct blow or injury to the Achilles tendon can cause tendinopathy.
It’s important to note that tendinopathy can develop gradually over time or suddenly, and may be caused by a combination of factors.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
The symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but some common symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain is the most common symptom of Achilles tendinopathy and is usually felt as a dull ache in the back of the leg or above the heel. The pain may be worse with activity and improve with rest.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the Achilles tendon and calf muscle may be present, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest.
- Swelling: Swelling may occur in the Achilles tendon and the surrounding area.
- Tenderness: The Achilles tendon may be tender to the touch, and there may be a palpable lump or thickening in the tendon.
- Limited range of motion: Reduced flexibility in the ankle joint may be present, making it difficult to fully flex or extend the foot.
- Crepitus: A creaking or cracking sensation may be felt in the Achilles tendon when it is moved.
It’s important to note that symptoms may worsen with activity, especially running, jumping, or other high-impact activities.
DIFFERENT WAYS TO DIAGNOSIS ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
There are several ways to diagnose Achilles tendinopathy, including:
- Physical examination: Your doctor will perform a physical examination to assess the extent of the damage to the Achilles tendon. This may involve feeling for lumps or thickening in the tendon, checking for pain and tenderness, and assessing your range of motion.
- Imaging tests: Your doctor may recommend imaging tests, such as an X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI, to get a more detailed look at the Achilles tendon and surrounding tissues.
- Functional tests: Your doctor may perform functional tests to evaluate your foot and ankle strength, flexibility, and balance, which can help determine the best course of treatment.
- Medical history: Your doctor will ask you about your medical history, including any previous injuries or medical conditions that may have contributed to the development of Achilles tendinopathy.
- Gait analysis: Your doctor may perform a gait analysis to assess your walking or running pattern, which can help identify any biomechanical issues that may be contributing to the development of Achilles tendinopathy.
It’s important to note that an accurate diagnosis is critical for proper treatment and management of Achilles tendinopathy from best phyiotherapist near you, most likely from hirephysio.com
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT FOR ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
The treatment for Achilles tendinopathy depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific needs. Some common treatments include:
- Rest: Rest is essential for allowing the Achilles tendon to heal. Activities that aggravate the tendon should be avoided, and rest periods should be incorporated into daily routines.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Compression can help reduce swelling and provide support to the Achilles tendon. Compression socks or wraps may be recommended.
- Elevation: Elevating the affected leg above the level of the heart can help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Exercises may be focused on stretching and strengthening the calf muscles and Achilles tendon.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotics, such as shoe inserts or braces, may be recommended to provide support and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is rarely necessary for Achilles tendinopathy, but in severe cases, it may be recommended to remove damaged tissue or repair the tendon.
HOW MUCH TIME IT TAKES TO TREAT ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY BY PHYSICAL THERAPY
The length of time it takes to treat Achilles tendinopathy with physical therapy can vary depending on the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and their adherence to the prescribed treatment plan. In general, physical therapy for Achilles tendinopathy may take several weeks to several months.
The initial phase of treatment typically focuses on reducing pain and inflammation through rest, ice, and other modalities, such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation. Once pain and inflammation have subsided, physical therapy may include exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the affected leg.
HOW TO MAKE ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY) HEAL FASTER OR RECOVER FASTER ?
There are several things you can do to help the healing process and recover faster from Achilles tendinopathy:
- Rest and reduce activity: Rest is essential for allowing the Achilles tendon to heal. Activities that aggravate the tendon should be avoided, and rest periods should be incorporated into daily routines. Reducing activity and avoiding high-impact exercises can also help reduce stress on the tendon.
- Ice and elevate: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Elevating the affected leg above the level of the heart can also help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the affected leg. Working with a physical therapist to develop a tailored exercise program can help speed up the recovery process.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotics, such as shoe inserts or braces, may be recommended to provide support and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Follow the prescribed treatment plan: It’s important to work closely with a healthcare professional and follow the prescribed treatment plan to achieve the best possible outcomes.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting adequate rest, and avoiding smoking can all help support the healing process.
It’s important to remember that recovery time can vary based on the severity of the condition and individual factors. It’s important to be patient and follow the prescribed treatment plan to allow the Achilles tendon to heal properly and reduce the risk of recurrence.
WHAT ARE THE PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
Here are the general steps a physiotherapist may take when treating Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy):
- Assessment: The physiotherapist will perform a thorough assessment of your condition, including asking about your symptoms and medical history, and conducting a physical examination. They may also use imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI to get a better view of the tendon.
- Pain relief: In the initial phase, the focus may be on reducing pain and inflammation through rest, ice, and other modalities, such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
- Stretching: Once pain and inflammation have subsided, the physiotherapist will focus on improving flexibility in the affected leg. Stretching exercises may be recommended to improve range of motion and reduce stiffness.
- Strengthening: The physiotherapist will also recommend strengthening exercises to improve the strength of the calf muscles and the Achilles tendon. Strengthening exercises may include toe raises, calf raises, and eccentric exercises.
- Gait analysis: The physiotherapist may analyze your gait (walking pattern) to determine if there are any abnormalities or imbalances that may be contributing to the condition. They may recommend gait retraining exercises to help correct these issues.
- Manual therapy: Manual therapy techniques such as massage, mobilization, or manipulation may be used to help improve circulation, reduce tension, and improve mobility in the affected leg.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotics, such as shoe inserts or braces, may be recommended to provide support and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Activity modification: The physiotherapist may recommend modifying activities or exercises that may be causing stress on the tendon, or suggest alternative exercises that are less likely to aggravate the condition.
- Gradual return to activity: As the Achilles tendon heals, the physiotherapist will help you gradually return to normal activities and exercise, while monitoring your progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
It’s important to note that the specific physiotherapy treatment plan will vary based on individual needs and the severity of the condition. A physiotherapist will develop a tailored treatment plan that takes into account your specific needs and goals, and work with you to help you recover from Achilles tendinopathy.
WHAT ARE THE CHIROPRACTOR TREATMENT FOR ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
Chiropractors may use a variety of treatment techniques to address Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy), including:
- Soft tissue therapy: This involves using manual techniques such as massage or myofascial release to help reduce muscle tension and promote healing of the affected area.
- Joint mobilization: Chiropractors may use joint mobilization techniques to help improve joint mobility and reduce pain and stiffness in the affected leg.
- Electrical stimulation: Chiropractors may use electrical stimulation therapy, such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), to help reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area.
- Ultrasound therapy: This involves using sound waves to help improve circulation and promote healing in the affected area.
- Exercise prescription: Chiropractors may prescribe specific exercises to help strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility in the affected leg.
- Taping: Chiropractors may use taping techniques, such as kinesiology taping, to help support the affected area and reduce stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Nutritional advice: Chiropractors may provide nutritional advice to help support the healing process and promote overall health and wellness.
WHAT ARE THE ACCUPRESSURE OR ACCUPUNTURIST TREATMENT FOR ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
Acupressure and acupuncture are forms of traditional Chinese medicine that involve the use of pressure or needles on specific points of the body to promote healing and reduce pain. While there is limited research on the effectiveness of these techniques for Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy), some acupressure or acupuncture points that may be targeted include:
- Gallbladder 34 (GB34): This point is located on the outer side of the lower leg, below the knee joint. It is believed to help reduce pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon.
- Bladder 60 (BL60): This point is located on the back of the ankle, between the Achilles tendon and the ankle bone. It is believed to help relieve pain and tension in the Achilles tendon.
- Kidney 3 (KD3): This point is located on the inner side of the ankle, just behind the ankle bone. It is believed to help promote healing and reduce inflammation in the Achilles tendon.
Acupressure techniques may involve applying pressure to these points using the hands, fingers, or specialized tools. Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into these points to stimulate the flow of energy (Qi) and promote healing.
WHAT ARE YOGA TREATMENT FOR ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
Yoga can be a helpful complementary therapy for Achilles tendinopathy, as it can help improve flexibility, strength, and balance, which are all important factors in preventing and treating this condition. Some yoga poses that may be beneficial for Achilles tendinopathy include:
- Downward-Facing Dog (Adho Mukha Svanasana): This pose helps stretch the calf muscles and hamstrings, which can help relieve tension and pressure on the Achilles tendon.
- Warrior II (Virabhadrasana II): This pose helps strengthen the legs and improve balance, which can help reduce the risk of further injury to the Achilles tendon.
- Tree Pose (Vrikshasana): This pose helps improve balance and stability in the lower body, which can help reduce the risk of falls or other injuries that can exacerbate Achilles tendinopathy.
- Pigeon Pose (Eka Pada Rajakapotasana): This pose helps stretch the hip flexors and thigh muscles, which can help reduce tension and pressure on the Achilles tendon.
- Garland Pose (Malasana): This pose helps stretch the calf muscles and Achilles tendon, while also improving balance and flexibility in the lower body.
WHAT DO’S AND DON’TS ADVICE IS GIVEN TO PATIENTS HAVING ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
Patients with Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy) are typically given advice on what they should and should not do to manage their symptoms and promote healing. Here are some common do’s and don’ts for patients with Achilles tendinitis:
Do’s:
- Rest: Resting the affected leg is important to allow the tendon to heal. Avoid activities that cause pain or discomfort.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Use an ice pack for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises prescribed by a physiotherapist can help promote healing and prevent future injury.
- Wear appropriate footwear: Wearing shoes with proper arch support and cushioning can help reduce pressure on the Achilles tendon.
- Use heel lifts: In some cases, wearing a heel lift in the shoe of the affected leg can help reduce tension on the Achilles tendon.
- Take medication as prescribed: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medication may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
Don’ts:
- Avoid high-impact activities: Activities that involve running or jumping should be avoided until the tendon has healed.
- Don’t ignore pain: Pain is a signal that something is wrong. If you experience pain in the Achilles tendon, stop the activity and rest the affected leg.
- Don’t skip warm-up exercises: Adequate warm-up exercises can help reduce the risk of injury to the Achilles tendon.
- Don’t continue exercising through pain: Continuing to exercise through pain can make the condition worse and delay healing.
- Avoid wearing high heels: Wearing high heels can put additional stress on the Achilles tendon and exacerbate symptoms.
- Don’t smoke: Smoking has been linked to decreased blood flow, which can delay healing and increase the risk of complications.
RECOMMENDED EXERCISE MACHINES AND BOOKS FOR PATIENT TO BUY FOR THEMSELVES FOR QUICK REHABILITATION IN ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
Here are some general guidelines and considerations for selecting exercise machines and books for patients:
Exercise Machines:
- Calf Stretch Blocks: Calf stretch blocks can be used to stretch the Achilles tendon and calf muscles, helping to reduce pain and improve flexibility.
- Foam Rollers: Foam rollers can be used to massage the calf muscles, reducing muscle tension and promoting blood flow to the affected area.
- Resistance Bands: Resistance bands can be used to strengthen the calf muscles and Achilles tendon, which can help prevent future injury.
- Balance Boards: Balance boards can be used to improve balance and stability, which can help reduce the risk of future injury.
Books:
- “The Complete Guide to Stretching” by Christopher M. Norris: This book provides a comprehensive guide to stretching, including specific stretches for the Achilles tendon and calf muscles.
- “Treat Your Own Achilles Tendinitis” by Jim Johnson: This book provides step-by-step instructions for exercises and stretches that can be done at home to help manage Achilles tendinopathy.
- “Clinical Guide to Sports Injuries” by Roald Bahr and Sverre Mæhlum: This book provides information on the diagnosis and treatment of sports injuries, including Achilles tendinopathy, and includes specific exercises and rehabilitation protocols.
OTHER SIMILAR PHYSICAL THERAPY CONDITIONS RELATED TO ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
There are several other conditions that are related to Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy) and may require similar physical therapy treatments. These include:
- Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar fasciitis is an overuse injury that affects the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot. It is characterized by pain and stiffness in the heel and arch of the foot, particularly in the morning or after prolonged periods of standing.
- Shin Splints: Shin splints are a common overuse injury that affects the muscles and bones in the shin. They are characterized by pain and tenderness along the front or inside of the shin, particularly during or after exercise.
- Patellar Tendinitis: Patellar tendinitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is an overuse injury that affects the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the shinbone. It is characterized by pain and tenderness around the patellar tendon, particularly during activities that involve jumping or running.
- Rotator Cuff Tendinitis: Rotator cuff tendinitis is an overuse injury that affects the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint. It is characterized by pain and weakness in the shoulder, particularly during overhead movements.
Physical therapy treatments for these conditions may include similar interventions such as stretching, strengthening exercises, and manual therapy techniques to alleviate pain and improve function.
FAQ ON ACHILLES TENDINITIS (ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY)
Q: What is Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy)?
A: Achilles tendinitis, also known as Achilles tendinopathy, is a condition that causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Q: What causes Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy)?
A: Achilles tendinitis can be caused by overuse, improper footwear, poor training techniques, or sudden increases in physical activity. It can also be associated with certain medical conditions, such as arthritis or diabetes.
Q: What are the symptoms of Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy)?
A: Symptoms of Achilles tendinitis can include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the back of the ankle, particularly after exercise or activity. There may also be tenderness or a “crunching” sensation when moving the ankle.
Q: How is Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy) diagnosed?
A: Achilles tendinitis can be diagnosed through a physical examination, imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI, or a combination of both.
Q: What are the treatment options for Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy)?
A: Treatment options for Achilles tendinitis may include rest, ice, compression, elevation, physical therapy, medication, or in severe cases, surgery.
Q: How long does it take to recover from Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy)?
A: The recovery time for Achilles tendinitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment approach. In general, it can take several weeks to several months to recover fully.
Q: Can Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy) be prevented?
A: Yes, Achilles tendinitis can be prevented by properly stretching before exercise, wearing appropriate footwear, gradually increasing physical activity, and incorporating strengthening exercises into your routine.
Q: What other conditions are related to Achilles tendinitis (Achilles tendinopathy)?
A: Other conditions related to Achilles tendinitis may include plantar fasciitis, shin splints, patellar tendinitis, and rotator cuff tendinitis.
Q: What is Achilles tendon pain while walking?
A: Achilles tendon pain while walking is a common symptom of Achilles tendinitis. It can occur in the back of the heel or ankle and can be worsened by physical activity.
Q: When is Achilles tendonitis surgery necessary?
A: Surgery for Achilles tendonitis is usually only necessary for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. It may also be necessary in cases of a complete Achilles tendon rupture.
Q: What are some exercises for Achilles tendonitis?
A: Exercises for Achilles tendonitis may include calf stretches, eccentric heel drops, and resistance band exercises. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program.
Q: What is a ruptured Achilles tendon?
A: A ruptured Achilles tendon occurs when the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone tears or completely separates. It can be a painful and debilitating injury that may require surgery.
Q: What are some treatments for Achilles tendonitis?
A: Treatments for Achilles tendonitis may include rest, ice, compression, elevation, physical therapy, medication, or in severe cases, surgery.
Q: What muscles are involved in the Achilles tendon?
A: The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body and connects the calf muscles (the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles) to the heel bone.
Q: How can physical therapy help with Achilles tendonitis?
A: Physical therapy for Achilles tendonitis may include exercises to stretch and strengthen the calf muscles, massage and manual therapy, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
Q: What is Orthobullets and how does it relate to Achilles tendonitis?
A: Orthobullets is an educational website for healthcare professionals that provides information on various orthopedic conditions, including Achilles tendonitis. It may be used by healthcare professionals to learn about diagnosis, treatment options, and surgical techniques.
Q: Can Achilles tendonitis be prevented?
A: Achilles tendonitis can often be prevented by maintaining proper footwear, gradually increasing intensity and duration of physical activity, stretching before and after exercise, and incorporating strength training exercises for the calf muscles.
Q: How long does it take to recover from Achilles tendonitis?
A: Recovery time for Achilles tendonitis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment used. Mild cases may heal in a few weeks with rest and physical therapy, while more severe cases may take several months to fully recover.
Q: Is it safe to continue exercising with Achilles tendonitis?
A: It is generally safe to continue exercising with Achilles tendonitis, as long as the activity does not worsen the condition. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before continuing any physical activity.
Q: Can Achilles tendonitis lead to a ruptured tendon?
A: If left untreated, Achilles tendonitis can lead to a complete rupture of the tendon. It is important to seek treatment early to prevent further damage.
Q: What are some home remedies for Achilles tendonitis?
A: Home remedies for Achilles tendonitis may include rest, ice, compression, elevation, and gentle stretching exercises. Over-the-counter pain medication may also be used to relieve pain and inflammation.
Q: What are some risk factors for Achilles tendonitis?
A: Risk factors for Achilles tendonitis may include age, physical activity level, improper footwear, tight calf muscles, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
More Articles:
- 10 + ways Get Back Fast on Track with Expert Physiotherapy for Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Differentiating Between Ankle sprains and Achilles tendinopathy || Hirephysio.com
- 3 Way – Effective Treatment Options for Ankle Sprains: Get Quick Relief Now! || Hirephysio.com
- 3 Way – Effective Treatment Options for ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY : Get Quick Relief Now! || Hirephysio.com