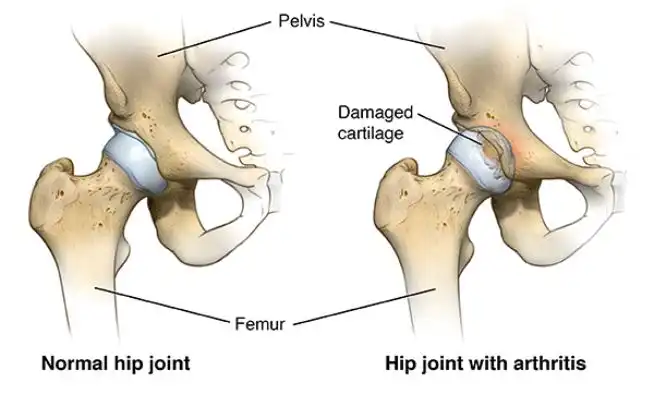
What is Hip osteoarthritis ?
Hip osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the hip joint, which is the joint that connects the thigh bone to the pelvis. It is a type of arthritis that results in the breakdown of cartilage, which is the cushioning material that covers the ends of the bones and helps them move smoothly against each other. As the cartilage wears away, the bones rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Hip osteoarthritis can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, genetics, injury, and obesity. It is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly those over 50 years of age. Treatment options for hip osteoarthritis include exercise, weight management, medication, and surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF Hip osteoarthritis?
The most common causes of hip osteoarthritis include:
- Age: As people age, the cartilage in the hip joint naturally wears down, making it more susceptible to osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: Some people may be more predisposed to developing hip osteoarthritis due to their genetic makeup.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts extra pressure on the hip joint, which can cause cartilage to break down more quickly.
- Injury: A hip injury, such as a fracture or dislocation, can increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis later in life.
- Repetitive stress: Activities that involve repetitive stress on the hip joint, such as long-distance running or playing certain sports, can also increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or avascular necrosis, can also increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis.
It is important to note that the development of hip osteoarthritis is often a combination of these factors rather than just one single cause.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
Hip osteoarthritis can cause a range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. Some common symptoms of hip osteoarthritis include:
- Pain in the hip joint that may worsen with activity or movement.
- Stiffness in the hip joint, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods.
- Reduced range of motion or difficulty moving the hip joint.
- A crunching or popping sensation in the hip joint.
- Swelling or tenderness around the hip joint.
- A feeling of weakness in the hip joint.
- Difficulty walking, especially uphill or on uneven surfaces.
- Reduced ability to participate in physical activities that require hip movement.
It is important to note that the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis can develop gradually over time, and they may not be noticeable at first. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare professional, such as a physiotherapist, for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
DIFFERENT WAYS TO DIAGNOSIS HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
There are several ways to diagnose hip osteoarthritis, including:
- Physical examination: A healthcare professional, such as a physiotherapist, will perform a physical examination of the hip joint to assess for any signs of osteoarthritis, such as reduced range of motion or tenderness around the joint.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, can help visualize the hip joint and determine the extent of any joint damage or cartilage loss.
- Joint fluid analysis: In some cases, a sample of the fluid in the hip joint may be taken and analyzed for signs of osteoarthritis.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms similar to hip osteoarthritis.
- Bone scans: Bone scans can detect any abnormalities in the bone around the hip joint that may be contributing to symptoms.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT FOR HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
There is currently no cure for hip osteoarthritis, but there are several treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Some common treatments for hip osteoarthritis include:
- Exercise: Regular exercise, including low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling, can help improve hip joint flexibility, strength, and overall function.
- Physical therapy: A physiotherapist can develop a personalized exercise plan and provide hands-on therapy to help manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms.
- Pain relief medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage hip pain and inflammation.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the hip joint can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Weight management: Losing weight, if necessary, can help reduce pressure on the hip joint and slow the progression of osteoarthritis.
- Assistive devices: Using assistive devices such as canes or walkers can help take pressure off the hip joint and improve mobility.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to replace the damaged hip joint with an artificial joint.
HOW MUCH TIME IT TAKES TO TREAT HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PHYSICAL THERAPY ?
The duration of physical therapy for hip osteoarthritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific needs and response to treatment. Some people may see improvement in their symptoms after just a few weeks of physical therapy, while others may require several months of ongoing therapy.
The goal of physical therapy for hip osteoarthritis is to improve hip joint function, reduce pain and stiffness, and increase overall mobility and quality of life. A physiotherapist will typically develop a personalized exercise plan based on the individual’s specific needs and goals, and will work with them to gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercises as tolerated.
It is important to note that physical therapy is not a quick fix for hip osteoarthritis and it may require ongoing commitment and effort to achieve long-term benefits. However, many people find that physical therapy can be an effective way to manage symptoms and improve overall hip joint function. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
WHAT ARE THE PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
Here are some common physiotherapy treatments for hip osteoarthritis, broken down step-by-step:
Initial Assessment: The first step in physiotherapy treatment for hip osteoarthritis is an initial assessment. This involves a thorough evaluation of the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and physical abilities. The physiotherapist will assess the range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the hip joint and surrounding muscles, as well as any areas of pain or discomfort.
Education and Advice: After the initial assessment, the physiotherapist will provide education and advice on ways to manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms. This may include information on exercise, activity modification, weight management, and the use of assistive devices such as canes or walkers.
Exercise Program: The next step in physiotherapy treatment for hip osteoarthritis is to develop a personalized exercise program. The exercise program may include a combination of exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and overall hip joint function. These exercises may include:
-
- Range-of-motion exercises: These exercises help to improve hip joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. Examples include hip circles and leg swings.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises help to build up the muscles around the hip joint, which can help improve joint stability and reduce pain. Examples include squats, lunges, and leg lifts.
- Low-impact exercises: Low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling can help improve overall fitness and hip joint function without putting too much stress on the joint.
Manual Therapy: In addition to exercises, a physiotherapist may use manual therapy techniques to help manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms. Manual therapy techniques may include:
-
- Joint mobilization: This involves gentle, passive movements of the hip joint to help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Soft tissue mobilization: This involves the use of massage or other manual techniques to help reduce muscle tension and improve overall hip joint function.
Pain Management: The physiotherapist may also provide pain management techniques to help manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms. This may include the use of heat or ice therapy, as well as the use of modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment: Finally, the physiotherapist will monitor the individual’s progress and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed. This may involve modifying exercises or techniques based on the individual’s response to treatment, as well as ongoing education and advice on ways to manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms.
It is important to note that the appropriate physiotherapy treatment for hip osteoarthritis will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific symptoms and needs.
WHAT ARE THE CHIROPRACTOR TREATMENT FOR HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
Chiropractic treatment for hip osteoarthritis can include a variety of techniques and therapies that aim to reduce pain, improve joint function, and increase mobility. Here are some common chiropractic treatments for hip osteoarthritis, broken down step-by-step:
- Initial Assessment: The first step in chiropractic treatment for hip osteoarthritis is an initial assessment. This involves a thorough evaluation of the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and physical abilities. The chiropractor will assess the range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the hip joint and surrounding muscles, as well as any areas of pain or discomfort.
- Chiropractic Adjustments: Chiropractic adjustments involve the use of hands-on manipulation techniques to help restore joint mobility, reduce pain, and improve function. The chiropractor will use gentle pressure or a sudden force to manipulate the hip joint in specific directions, depending on the individual’s symptoms and needs.
- Soft Tissue Therapy: Soft tissue therapy involves the use of massage or other manual techniques to help reduce muscle tension and improve overall hip joint function. The chiropractor may use techniques such as myofascial release or trigger point therapy to help reduce pain and stiffness in the muscles surrounding the hip joint.
- Exercise Program: The chiropractor may also develop a personalized exercise program to help improve hip joint function and reduce symptoms of hip osteoarthritis. This may include a combination of exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and overall hip joint function.
- Nutrition and Lifestyle Advice: The chiropractor may provide advice on nutrition and lifestyle changes that can help reduce symptoms of hip osteoarthritis. This may include recommendations for weight management, stress reduction, and other lifestyle modifications that can help improve overall joint health.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment: Finally, the chiropractor will monitor the individual’s progress and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed. This may involve modifying chiropractic techniques or exercises based on the individual’s response to treatment, as well as ongoing education and advice on ways to manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms.
It is important to note that the appropriate chiropractic treatment for hip osteoarthritis will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific symptoms and needs.
WHAT ARE THE ACCUPRESSURE OR ACCUPUNTURIST TREATMENT FOR HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
Acupressure and acupuncture are complementary therapies that can be used to treat hip osteoarthritis. Both techniques involve the application of pressure or needles to specific points on the body to help reduce pain and improve joint function. Here are the steps involved in acupressure or acupuncture treatment for hip osteoarthritis:
- Assessment: The first step in acupressure or acupuncture treatment for hip osteoarthritis is an assessment of the individual’s symptoms and medical history. This will help the acupressure or acupuncture practitioner determine which points on the body to target with pressure or needles.
- Identification of Pressure Points: The practitioner will identify specific points on the body that correspond to the hip joint and surrounding muscles. These points may be located on the hip itself, as well as on other areas of the body that are connected to the hip joint.
- Application of Pressure or Needles: In acupressure, the practitioner will use their hands, fingers, or other tools to apply pressure to the identified points on the body. In acupuncture, the practitioner will insert small needles into the same points. Both techniques aim to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and reduce pain and inflammation in the hip joint.
- Stimulation: Once the pressure or needles are in place, the practitioner may use various techniques to stimulate the points. This may include gentle manipulation or movement of the needles, or the use of heat or electrical stimulation.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: During the treatment, the practitioner will monitor the individual’s response to the pressure or needles and adjust the treatment as needed. This may involve targeting different pressure points, adjusting the intensity of the pressure or stimulation, or modifying the treatment schedule.
- Lifestyle Advice: In addition to acupressure or acupuncture treatment, the practitioner may provide advice on lifestyle modifications that can help reduce symptoms of hip osteoarthritis. This may include recommendations for diet, exercise, stress reduction, and other complementary therapies.
It is important to note that acupressure and acupuncture are not suitable for everyone and may not be appropriate for individuals with certain medical conditions.
WHAT ARE YOGA TREATMENT FOR HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
Yoga can be a helpful complementary therapy for managing hip osteoarthritis. It can help improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the hip joint, as well as reduce pain and inflammation. Here are the steps involved in a yoga treatment for hip osteoarthritis:
Assessment: The first step in using yoga as a treatment for hip osteoarthritis is an assessment of the individual’s symptoms and medical history. This will help the yoga practitioner determine which poses to include in the practice and how to modify them to accommodate any limitations or restrictions.
Warm-Up: Before starting the yoga practice, it is important to warm up the body to prepare the joints and muscles for movement. This may involve gentle stretching, breathing exercises, or other techniques to increase circulation and loosen up the body.
Hip-Opening Poses: The main focus of a yoga practice for hip osteoarthritis is on hip-opening poses that help stretch and strengthen the muscles around the hip joint. This may include poses such as:
-
- Pigeon Pose
- Triangle Pose
- Warrior II Pose
- Bound Angle Pose
These poses can help improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and increase range of motion in the hip joint.
Strengthening Poses: In addition to hip-opening poses, it is important to include strengthening poses that target the muscles around the hip joint. This may include poses such as:
-
- Bridge Pose
- Chair Pose
- Warrior I Pose
- Tree Pose
These poses can help improve stability and support for the hip joint, which can help reduce pain and prevent further damage.
Relaxation and Breathing: At the end of the yoga practice, it is important to include relaxation and breathing exercises to help reduce stress and promote healing. This may involve poses such as:
-
- Corpse Pose
- Child’s Pose
- Seated Meditation
These poses can help calm the mind and reduce tension in the body, which can help improve overall wellbeing.
It is important to note that yoga is not suitable for everyone and may not be appropriate for individuals with certain medical conditions.
WHAT DO’S AND DON’TS ADVICE IS GIVEN TO PATIENTS HAVING HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS ?
Here are some general dos and don’ts advice for patients with hip osteoarthritis:
Do’s:
- Stay active and engage in low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to help maintain joint mobility and reduce pain.
- Use assistive devices, such as a cane or walker, to help reduce stress on the hip joint.
- Maintain a healthy body weight to reduce pressure on the hips.
- Use heat or cold therapy to help alleviate pain and stiffness.
- Work with a physiotherapist to develop a customized exercise program to help improve joint function and range of motion.
Don’ts:
- Engage in high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, that can put stress on the hip joint and exacerbate symptoms.
- Sit or stand for prolonged periods of time, as this can cause stiffness and discomfort.
- Lift heavy objects or engage in activities that require a lot of bending and twisting.
- Ignore your symptoms or delay seeking medical attention, as this can lead to further joint damage and pain.
WHAT ARE THE RECOMMENDED SIMPLE EXERCISE MACHINES , BOOKS , OTHERS FOR HIP OSTEOARTHRITISPERSON FOR EASY AND QUICK TREATMENT OR RECOVERY?
Some recommended simple exercise machines, books, and other resources for individuals with hip osteoarthritis:
Exercise Machines:
-
- Elliptical Trainer: This low-impact machine provides a great cardiovascular workout without putting stress on the hip joint.
- Stationary Bike: Another low-impact machine that provides a great cardiovascular workout and helps improve hip joint mobility.
- Resistance Bands: These bands can be used for various strengthening exercises that target the hip muscles.
Books:
-
- “The Arthritis Foundation’s Guide to Good Living with Osteoarthritis” by Nancy Ann Shadick: This book provides comprehensive information on osteoarthritis, including tips on managing symptoms and improving joint function.
- “Exercises for Osteoarthritis” by William Smith and Edward Phillips: This book provides a range of exercises that can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain associated with osteoarthritis.
Other Resources:
-
- Arthritis Foundation: This non-profit organization offers a range of resources and information on managing osteoarthritis, including exercise programs and online support groups.
- Online Physiotherapy Services: Virtual physiotherapy services can provide individuals with customized exercise programs and expert guidance on managing hip osteoarthritis from the comfort of their own homes.
OTHER SIMILAR PHYSICAL THERAPY CONDITIONS RELATED TO HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS?
There are several other physical therapy conditions that are related to hip osteoarthritis. Some of these conditions include:
- Trochanteric Bursitis: This is a condition where the bursa (a small fluid-filled sac) that lies over the bony point on the side of the hip becomes inflamed, leading to pain and tenderness in the hip joint.
- Hip Labral Tear: This is a tear in the labrum, which is a ring of cartilage that lines the socket of the hip joint. This can lead to pain, clicking or catching sensations, and decreased range of motion in the hip joint.
- Hip Flexor Strain: This is a strain or tear in one of the hip flexor muscles, which are responsible for lifting the leg and bending the hip. This can lead to pain in the front of the hip, and may also cause difficulty with walking or other activities that require hip flexion.
- Piriformis Syndrome: This is a condition where the piriformis muscle, which runs from the lower back to the top of the hip joint, becomes tight or inflamed and compresses the sciatic nerve. This can lead to pain in the hip, buttocks, and down the back of the leg.
- Hip Impingement: This is a condition where there is abnormal contact between the bones of the hip joint, leading to pain and reduced range of motion.
Physiotherapy treatment for these conditions may vary, but often includes exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the hip joint, as well as manual therapy techniques and modalities to reduce pain and inflammation.
FAQ ON HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS
Q: What is hip osteoarthritis?
A: Hip osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the hip joint, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Q: How is hip osteoarthritis diagnosed?
A: Hip osteoarthritis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI.
Q: What are the treatment options for hip osteoarthritis?
A: Treatment options for hip osteoarthritis include physical therapy, medications, injections, and in severe cases, surgery.
Q: What types of exercises are recommended for hip osteoarthritis?
A: Exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles around the hip joint, such as hip abductor and adductor exercises, are often recommended for hip osteoarthritis.
Q: Is it safe to exercise with hip osteoarthritis?
A: Yes, it is safe to exercise with hip osteoarthritis as long as you follow a program that is designed specifically for your condition and avoid high-impact activities that could exacerbate your symptoms.
Q: Can physical therapy prevent the need for surgery for hip osteoarthritis?
A: Yes, physical therapy can be effective in reducing pain and improving mobility, which can in turn delay or even prevent the need for surgery.
Q: How long does physical therapy take to show results for hip osteoarthritis?
A: The duration of physical therapy for hip osteoarthritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment, but significant improvements can often be seen within a few weeks to a few months.
Q: What are some new treatments for hip osteoarthritis?
A: Some new treatments for hip osteoarthritis include stem cell therapy, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, and minimally invasive hip surgery. These treatments are aimed at reducing pain and inflammation, promoting healing, and improving function and mobility of the hip joint.
Q: What are the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis?
A: The symptoms of hip osteoarthritis include pain in the hip joint that worsens with activity or movement, stiffness in the hip joint especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods, reduced range of motion or difficulty moving the hip joint, a crunching or popping sensation in the hip joint, swelling or tenderness around the hip joint, a feeling of weakness in the hip joint, difficulty walking, and reduced ability to participate in physical activities that require hip movement.
Q: Can physical therapy help with hip osteoarthritis?
A: Yes, physical therapy can be an effective treatment for hip osteoarthritis. Physical therapists can design personalized exercise programs aimed at reducing pain and inflammation, improving flexibility and strength, and increasing mobility and function of the hip joint. They may also use modalities such as heat, cold, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation to help relieve pain and promote healing.
Q: Is surgery necessary for hip osteoarthritis?
A: Surgery may be recommended for hip osteoarthritis if conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications have not provided sufficient relief from symptoms. However, surgery is typically considered a last resort and is not always necessary for all cases of hip osteoarthritis. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic surgeon, to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
More articles:
- 10 + ways Get Back Fast on Track with Expert Physiotherapy for Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Quick Understanding of Hip Osteoarthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment | No. 1 Hirephysio.com
- Easy Cure of Hip and knee osteoarthritis with number 1 Hirephysio Physiotherapy Centre