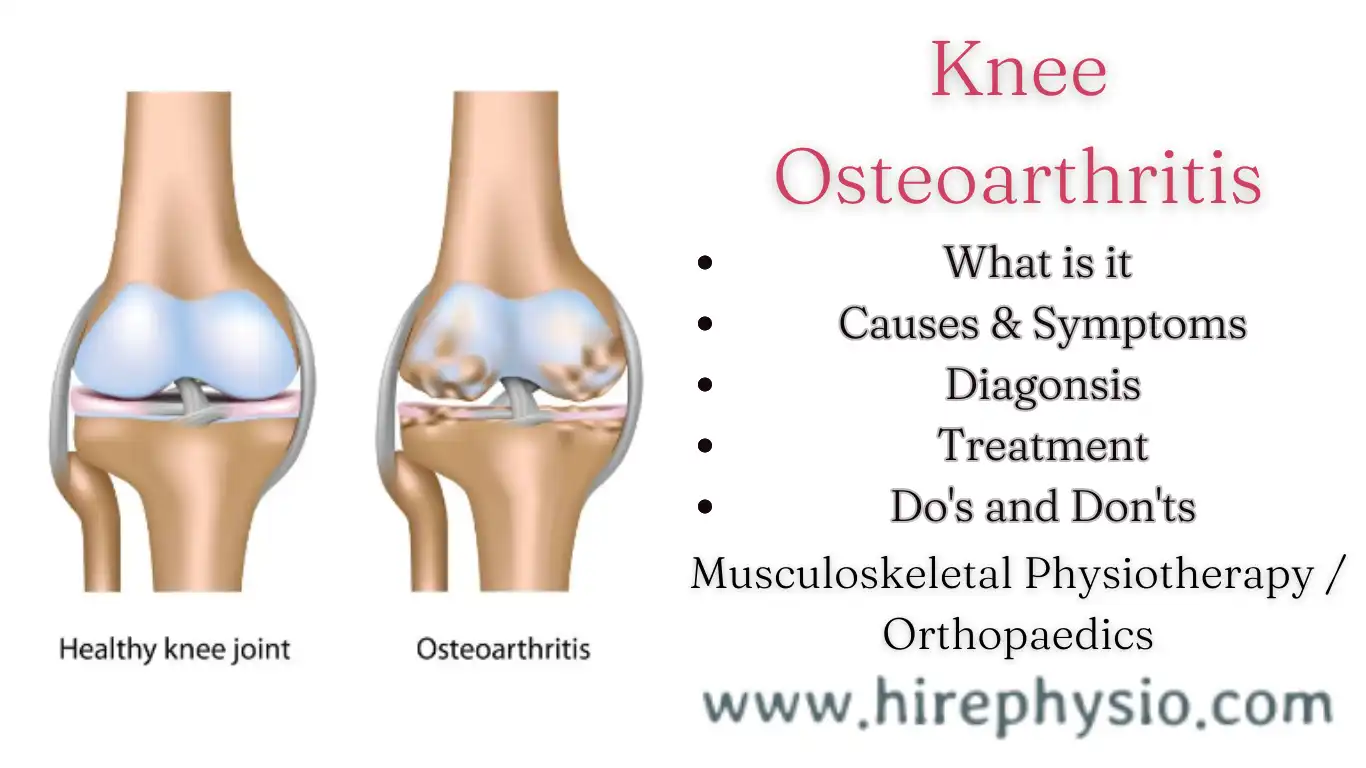
What is knee osteoarthritis?
Knee osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative joint disease of the knee, is a common condition that can cause significant pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the knee joint. It occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee gradually wears away, leading to bone-on-bone contact and inflammation. While there is no cure for knee osteoarthritis, there are many treatments and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. At Hirephysio.com, our team of skilled physiotherapists can help you develop a comprehensive treatment plan to manage your knee osteoarthritis and improve your quality of life.
What are the causes of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the knee ?
The exact causes of knee osteoarthritis are not fully understood, but there are several factors that can contribute to its development, including:
- Age: As people age, the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis increases. This is because the cartilage in the knee joint tends to wear down over time.
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing knee osteoarthritis due to genetic factors. For example, if a person has a family history of the condition, they may be more likely to develop it themselves.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can put extra stress on the knee joint, which can accelerate the wear and tear of the cartilage.
- Previous knee injuries: People who have had previous knee injuries, such as a torn meniscus or ligament damage, may be at a higher risk of developing knee osteoarthritis later in life.
- Repetitive stress: People who engage in activities that place repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as running or jumping, may be more likely to develop knee osteoarthritis.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or Paget’s disease, can increase the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop knee osteoarthritis than men. This may be due to differences in hormonal and biomechanical factors.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE
Knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the knee can cause a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity depending on the stage of the condition. Some common symptoms of knee osteoarthritis include:
- Pain in the knee joint, which can be dull or sharp and may worsen with activity or prolonged sitting or standing.
- Stiffness in the knee joint, which may be worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Swelling or inflammation in the knee joint, which may be accompanied by warmth or redness.
- Crunching or popping sensations in the knee joint during movement.
- Limited range of motion in the knee joint, which may make it difficult to bend or straighten the leg.
- Weakness in the leg, particularly if the knee joint is unstable or if there is muscle wasting around the knee.
- Difficulty with daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis can vary from person to person, and some people may experience few or no symptoms at all. So, Physiotherapits adivce is must.
DIFFERENT WAYS TO DIAGNOSIS KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
There are several different ways to diagnose knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the knee, including:
- Physical examination: Your doctor or physiotherapist will perform a physical examination of your knee joint to check for signs of pain, swelling, stiffness, or limited range of motion. They may also assess your gait and look for any abnormalities in the way you walk.
- X-rays: X-rays of the knee joint can provide detailed images of the bones and cartilage, allowing your healthcare provider to assess the extent of any joint damage or degeneration.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI scan can provide more detailed images of the soft tissues in the knee joint, including the cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
- Joint fluid analysis: Your healthcare provider may use a needle to withdraw a sample of fluid from your knee joint and analyze it for signs of inflammation or infection.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to rule out other possible causes of joint pain and inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging can be used to assess the soft tissues in and around the knee joint, such as the cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
Diagnosing knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the knee typically involves a combination of these methods. Your healthcare provider or physiotherapist can work with you to determine the most appropriate diagnostic approach based on your individual symptoms and medical history.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT FOR KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
The treatment options for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the knee depend on the severity of the condition, as well as individual factors such as age, lifestyle, and overall health. Here are some common treatment options:
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can help you develop an exercise program to improve the strength and flexibility of the muscles surrounding the knee joint. They can also provide manual therapy and other techniques to help reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Weight management: Excess weight can place additional stress on the knee joint, exacerbating symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. Losing weight can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Medications: Pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee joint. In some cases, your healthcare provider may also prescribe corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
- Assistive devices: Using a cane, brace, or other assistive device can help reduce stress on the knee joint and improve stability.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joint tissue. Knee replacement surgery involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial joint.
- Lifestyle modifications: Certain lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding high-impact activities or modifying daily activities to reduce stress on the knee joint, can help manage symptoms of knee osteoarthritis.
HOW MUCH TIME IT TAKES TO TREAT KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE BY PHYSICAL THERAPY ?
In general, a physical therapy program for knee osteoarthritis or DJD may last for several weeks to several months, to be precise, it depends on person to person and individual case.
WHAT ARE THE PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
Some of the common physiotherapy treatments for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease:
- Evaluation and Assessment: The first step in physiotherapy treatment for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease is to conduct a thorough evaluation and assessment. This typically involves a physical examination, range of motion testing, and evaluation of functional limitations. The physiotherapist will also take into account any previous medical history and imaging reports.
- Pain Management: One of the primary goals of physiotherapy treatment for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease is pain management. The physiotherapist may use a variety of techniques to help manage pain, including hot and cold therapy, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or massage. Additionally, the therapist may recommend lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, to help alleviate pressure on the affected joint.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening exercises are an essential part of the physiotherapy treatment plan for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint, which can help improve joint stability and function. The physiotherapist will develop a customized exercise program based on the individual’s specific needs and abilities.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Range of motion exercises are designed to help improve flexibility and mobility in the affected joint. The physiotherapist may use various techniques such as stretching, manual therapy, or joint mobilization to help improve range of motion.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: Balance and proprioception training is a crucial component of physiotherapy treatment for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. This type of training is designed to improve balance and coordination, which can help reduce the risk of falls and improve overall joint function.
- Gait Training: Gait training involves analyzing the individual’s walking pattern and identifying any abnormalities or imbalances. The physiotherapist will develop a customized plan to help correct any gait abnormalities and improve overall walking function.
- Assistive Devices: In some cases, the physiotherapist may recommend the use of assistive devices such as knee braces, crutches, or walkers to help support the affected joint and reduce pain.
It’s important to note that each individual’s physiotherapy treatment plan may vary based on their specific needs and goals.
WHAT ARE THE CHIROPRACTOR TREATMENT FOR KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
Chiropractic treatment for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease typically involves a combination of manual therapies, exercises, and lifestyle modifications. Here are some common chiropractic treatments for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease:
- Manual Therapy: Manual therapy techniques are commonly used by chiropractors to help alleviate pain and stiffness in the affected joint. This may include joint manipulation, mobilization, or soft tissue therapy such as massage.
- Exercise Therapy: Exercise therapy is an essential part of chiropractic treatment for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Chiropractors may prescribe exercises designed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint, improve flexibility and range of motion, and improve overall function.
- Nutritional and Lifestyle Counseling: Chiropractors may also provide nutritional and lifestyle counseling to help individuals manage knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. This may include recommendations for weight loss, dietary changes, and exercise modifications to help reduce stress on the affected joint.
- Assistive Devices: Chiropractors may also recommend the use of assistive devices such as knee braces or orthotics to help support the affected joint and improve overall function.
WHAT ARE THE ACCUPRESSURE OR ACCUPUNTURIST TREATMENT FOR KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
Acupressure and acupuncture are alternative therapies that involve the stimulation of specific points on the body to help manage symptoms of various health conditions, including knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Here are some common acupressure and acupuncture treatments for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease:
- Local Point Stimulation: Acupressure and acupuncture may involve the stimulation of specific points on or near the knee joint to help alleviate pain and improve function. These points may be stimulated using pressure or small, sterile needles.
- Meridian Therapy: Meridian therapy is a form of acupuncture that involves the stimulation of specific points along energy pathways (meridians) in the body to help promote healing and balance. Acupuncturists may use meridian therapy to help manage symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease.
- Electroacupuncture: Electroacupuncture involves the use of small electric currents applied to acupuncture needles to help stimulate specific points on the body. This may help promote pain relief and reduce inflammation in the affected joint.
- Moxibustion: Moxibustion is a traditional Chinese therapy that involves the burning of dried herbs (usually mugwort) on or near the skin to help promote healing and reduce pain and inflammation. Moxibustion may be used in combination with acupuncture or acupressure to help manage symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease.
WHAT ARE YOGA TREATMENT FOR KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
Yoga is a form of exercise that involves physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, and it can be beneficial for individuals with knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Here are some common yoga practices that may help manage symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease:
- Gentle Yoga Poses: Gentle yoga poses can help improve flexibility, strength, and balance, which are all important for managing knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Some examples of gentle yoga poses include seated forward fold, seated twist, and reclining leg stretch.
- Restorative Yoga: Restorative yoga involves the use of props such as blankets, blocks, and bolsters to support the body in various poses, promoting relaxation and healing. Restorative yoga can be especially beneficial for individuals with knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease, as it can help reduce stress on the affected joint.
- Pranayama (Breathing Techniques): Pranayama, or breathing techniques, can help improve lung function and reduce stress, both of which can be beneficial for individuals with knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Some common pranayama techniques include deep breathing, alternate nostril breathing, and kapalabhati breathing.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being, which may help individuals better manage symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Some examples of mindfulness meditation practices include body scans, walking meditation, and loving-kindness meditation.
WHAT DO’S AND DON’TS ADVICE IS GIVEN TO PATIENTS HAVING KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
Patients with knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease may be given the following do’s and don’ts advice to help manage their condition:
Do’s:
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected joint. Low-impact activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming may be particularly beneficial.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can place additional stress on the knee joint, exacerbating symptoms of osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce this stress and improve overall joint health.
- Use assistive devices: Assistive devices such as knee braces, crutches, or canes can help reduce stress on the affected joint and improve mobility.
- Follow a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids can help improve joint health and reduce inflammation.
- Get plenty of rest: Rest is important for allowing the body to heal and repair damaged joint tissue. Getting enough sleep and taking breaks when needed during the day can help manage symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease.
Don’ts:
- Avoid high-impact activities: High-impact activities such as running, jumping, or contact sports can place excessive stress on the knee joint, worsening symptoms of osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease.
- Don’t overdo it: While exercise is important, it’s also important to avoid overexertion, which can exacerbate symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Be sure to listen to your body and take breaks when needed.
- Avoid sitting or standing for long periods of time: Prolonged periods of sitting or standing can place additional stress on the knee joint, exacerbating symptoms of osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Be sure to take frequent breaks and change positions often.
- Don’t ignore pain or discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the knee joint can be a sign that the joint is being overstressed. It’s important to listen to your body and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or do not improve with self-care measures.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking has been linked to increased inflammation in the body, which can worsen symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Quitting smoking can help improve joint health and reduce inflammation.
OTHER SIMILAR PHYSICAL THERAPY CONDITIONS RELATED TO KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE ?
There are several other similar physical therapy conditions related to knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. Some of these conditions include:
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a condition that causes pain in the front of the knee, often due to overuse or improper alignment of the patella (kneecap). Physical therapy for patellofemoral pain syndrome may include exercises to improve strength and flexibility of the quadriceps and hip muscles, as well as manual therapy and taping techniques to help realign the patella.
- Meniscus Tear: A meniscus tear is a common knee injury that occurs when the meniscus, a rubbery cartilage that cushions the knee joint, is torn. Physical therapy for a meniscus tear may include exercises to improve strength and flexibility of the quadriceps and hamstring muscles, as well as balance and proprioceptive exercises to improve joint stability.
- ACL Tear: An ACL tear is a serious knee injury that occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is torn. Physical therapy for an ACL tear may include exercises to improve strength and flexibility of the quadriceps and hamstring muscles, as well as proprioceptive and balance exercises to improve joint stability.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and joint pain throughout the body, including the knee joint. Physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis may include exercises to improve joint mobility and flexibility, as well as strength training exercises to help support the joint.
- Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Physical therapy for gout may include exercises to improve joint mobility and flexibility, as well as strength training exercises to help support the joint and reduce inflammation.
RECOMMENDED EXERCISE MACHINES AND BOOKS FOR PATIENT TO BUY FOR THEMSELVES FOR QUICK REHABILITATION IN KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE
Exercise Machines:
-
- Stationary bike: a low-impact exercise that can help improve knee range of motion, strength, and flexibility.
- Elliptical machine: low-impact exercise that can help improve cardiovascular fitness, lower body strength, and range of motion.
- Rowing machine: low-impact exercise that can help improve cardiovascular fitness, upper body strength, and core stability.
- Leg press machine: a resistance machine that targets the quadriceps muscles of the legs, which can help improve knee strength.
Books:
-
- “The Arthritis Handbook: Improve Your Health and Manage the Pain of Osteoarthritis” by Grant Cooper: This book provides information on managing arthritis pain, exercises for reducing stiffness and improving joint mobility, and advice on diet and lifestyle changes that may help reduce inflammation.
- “Exercises for Osteoarthritis: A Safe and Effective Way to Reduce Pain and Improve Mobility” by William Smith: This book provides a variety of exercises specifically designed for people with osteoarthritis, including exercises for the knees, hips, and spine.
- “The Knee Owner’s Manual: Everything You Need to Know About Knee Health” by Dr. Jim Johnson: This book provides information on knee anatomy, common knee problems, and exercises for improving knee strength, flexibility, and stability.
FAQ ON KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS OR DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE
Q: What is knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease?
A: Knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease is a degenerative condition that occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Q: What are the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease?
A: Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease may include pain, stiffness, swelling, clicking or popping sounds, reduced mobility, and difficulty with activities such as walking, bending, or climbing stairs.
Q: What causes knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease?
A: Knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, genetics, obesity, joint injuries, and overuse.
Q: How is knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease diagnosed?
A: Knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease is typically diagnosed through a combination of a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans.
Q: What are the treatment options for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease?
A: Treatment options for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease may include physical therapy, medication, weight loss, assistive devices such as knee braces, and in severe cases, surgery.
Q: Can knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease be prevented?
A: While there is no surefire way to prevent knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding joint injuries, and wearing proper footwear can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Q: Is knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease curable? A: While there is no cure for knee osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease, treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve joint function, allowing individuals to maintain an active lifestyle.
More articles:
- 10 + ways Get Back Fast on Track with Expert Physiotherapy for Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Quick Understanding of Hip Osteoarthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment | No. 1 Hirephysio.com
- Easy Cure of Hip and knee osteoarthritis with number 1 Hirephysio Physiotherapy Centre