Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – Easy, effective and affordable treatment using physiotherapy
As a leading physiotherapy website, HirePhysio.com aims to provide you with valuable information about various health conditions and how physiotherapy can help manage them. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and other autoimmune disorders can be debilitating conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. These disorders can cause chronic pain, joint stiffness, and mobility limitations, making daily activities challenging.
Physiotherapy can play a vital role in managing these conditions by providing customized exercise programs, manual therapy, and education to improve joint mobility, muscle strength, and function. Our experienced physiotherapists can work with you to develop a comprehensive treatment plan to help you manage your RA or autoimmune disorder effectively. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how physiotherapy can help you lead a more active and pain-free life.
WHAT IS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OTHER AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERSIN PHYSIOTHERAPY AND HOW THEY DIFFER FROM EACH OTHER
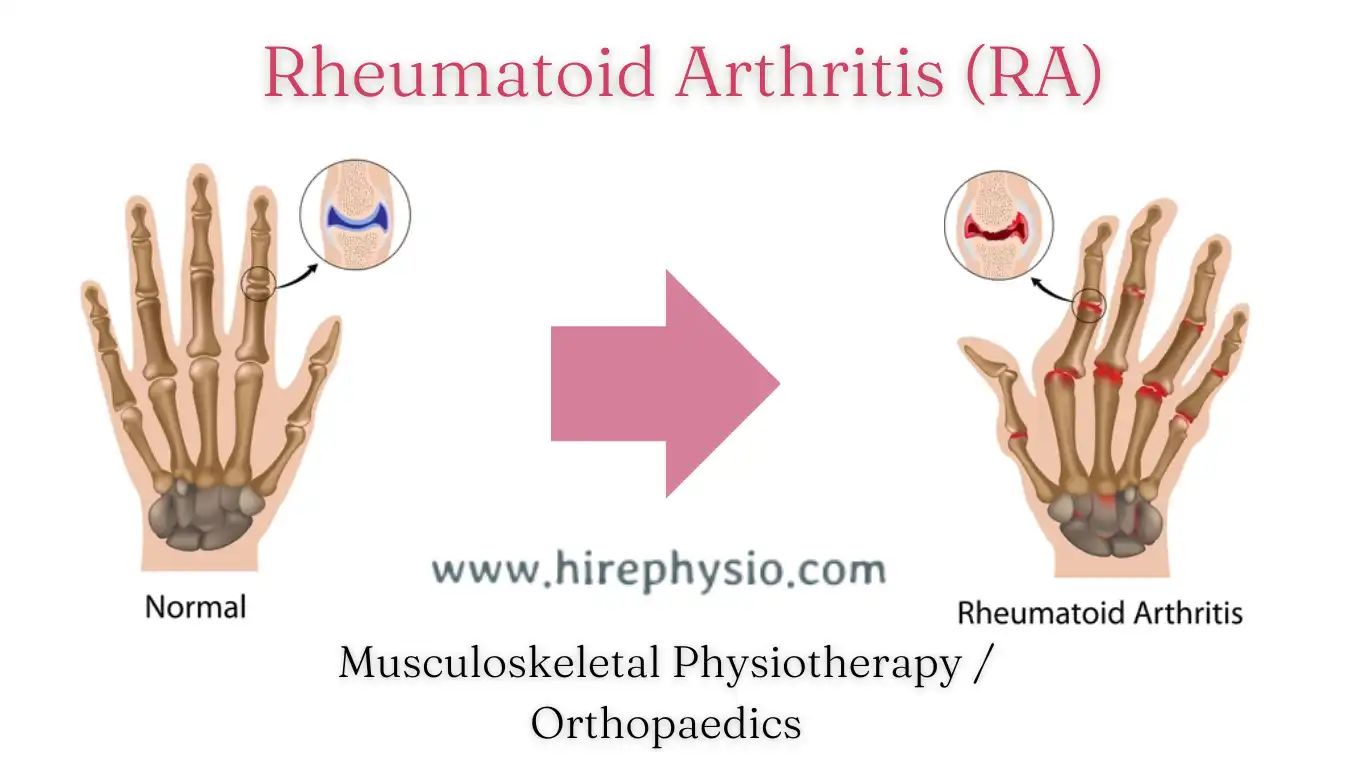
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. The immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial lining of the joints, resulting in erosion of cartilage and bone. RA can also affect other organs, such as the lungs, heart, and skin. Physiotherapy can help manage RA symptoms by providing exercise programs that can improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
Other autoimmune disorders are conditions where the immune system attacks healthy cells in the body, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. These disorders can affect different organs and systems, leading to a variety of symptoms. Examples of autoimmune disorders include lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. Physiotherapy can be an effective way to manage these conditions by providing exercises that can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and balance.
The key difference between rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disorders is that RA primarily affects the joints, while other autoimmune disorders can affect various organs and tissues in the body. While physiotherapy can be helpful in managing the symptoms of both RA and other autoimmune disorders, the treatment plan needs to be tailored to the specific condition and individual needs of the patient. A physiotherapist can work with patients to develop a customized exercise program and manual therapy to help manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
WHAT KIND OF PEOPLE USUALLY GETS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PHYSIOTHERAPY
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a type of autoimmune disorder that can affect people of all ages, genders, and races. However, certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing RA. These factors include:
- Gender: RA is more commonly diagnosed in women than in men.
- Age: RA typically occurs in people between the ages of 40 and 60 years.
- Family history: People with a family history of RA are more likely to develop the condition.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing RA.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing RA.
It is important to note that anyone can develop RA, regardless of age, gender, or other risk factors. RA can be a challenging condition to manage, but physiotherapy can be a helpful way to manage the symptoms of RA and improve quality of life.
HOW DO I KNOW IF A PERSON IS AFFECTED BY RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OR SOME OTHER AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS
It can be difficult to know if a person is affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or other autoimmune disorders as the symptoms can vary widely and may not always be obvious. However, there are some common signs and symptoms to look out for, including:
- Joint pain and stiffness: RA typically affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling, particularly in the hands, wrists, and feet. Other autoimmune disorders may also cause joint pain and stiffness.
- Fatigue: People with RA and other autoimmune disorders often experience fatigue, which can range from mild to severe.
- Skin rashes: Certain autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and psoriasis, can cause skin rashes.
- Muscle weakness: Some autoimmune disorders, such as myasthenia gravis, can cause muscle weakness.
- Digestive problems: Autoimmune disorders such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can cause digestive problems.
- Numbness and tingling: Some autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, can cause numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. A doctor can perform tests and exams to help determine if an autoimmune disorder is present and provide appropriate treatment options.
Physiotherapy can also be an effective way to manage the symptoms of many autoimmune disorders, particularly those that affect the joints or muscles. A physiotherapist can work with individuals to create a customized exercise program and provide manual therapy to reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall physical function.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
The exact cause of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissue. In the case of RA, the immune system attacks the synovium, which is the lining of the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness.
Some factors that may contribute to the development of RA include:
- Genetics: People with a family history of RA are more likely to develop the condition.
- Environment: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as smoking or pollution, may increase the risk of developing RA.
- Hormones: Women are more likely to develop RA than men, which suggests that hormones may play a role in the development of the condition.
- Age: RA typically occurs in people between the ages of 40 and 60 years.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing RA.
While these factors may increase the likelihood of developing RA, they do not guarantee that someone will develop the condition.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, but it can also affect other parts of the body. The symptoms of RA can vary widely from person to person, but some common signs and symptoms include:
- Joint pain and stiffness: RA typically causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints, particularly in the hands, wrists, and feet. The symptoms are usually symmetrical, meaning that they occur in the same joints on both sides of the body.
- Fatigue: Many people with RA experience fatigue, which can range from mild to severe and can be debilitating.
- Morning stiffness: People with RA often experience stiffness in the joints, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Limited range of motion: RA can cause the joints to become stiff and difficult to move, which can limit mobility and range of motion.
- Rheumatoid nodules: Some people with RA develop small, firm bumps under the skin, known as rheumatoid nodules.
- Eye problems: RA can cause inflammation in the eyes, leading to dryness, redness, and other eye problems.
- Fever: Some people with RA may experience a low-grade fever.
DIFFERENT WAYS TO DIAGNOSIS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) can be a challenging condition to diagnose, as its symptoms can vary widely from person to person, and there is no single test that can definitively confirm the presence of RA. However, there are several ways that physiotherapists can help to diagnose RA and develop an appropriate treatment plan:
- Medical history and physical exam: A physiotherapist will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical exam to assess joint mobility, pain, and other symptoms.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help to identify specific antibodies that are commonly present in people with RA, including rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRI scans can help to identify joint damage and inflammation.
- Joint aspiration: A joint aspiration involves using a needle to remove fluid from a joint, which can help to diagnose RA and rule out other conditions.
- Collaboration with a physician: A physiotherapist may work closely with a patient’s primary care physician or rheumatologist to develop an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of RA, as early diagnosis and treatment can help to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
There is currently no cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), but there are several treatment options available to help manage its symptoms and slow its progression. The following are some of the most common treatments for RA:
- Medications: There are several types of medications that can help to manage RA symptoms, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents.
- Physical therapy: A physiotherapist can develop an individualized exercise program to help improve joint mobility, reduce pain and inflammation, and increase overall physical function.
- Occupational therapy: An occupational therapist can help individuals with RA to develop strategies for managing everyday tasks and activities, such as dressing, cooking, and cleaning.
- Assistive devices: Devices such as braces, splints, and mobility aids can help to reduce joint pain and improve mobility.
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and stress management techniques, can help to manage RA symptoms and improve overall health.
- Surgery: In severe cases of RA, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
HOW MUCH TIME IT TAKES TO TREAT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PHYSIOTHERAPY BY PHYSICAL THERAPY
The treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) with physical therapy varies depending on the severity of the condition, response to treatment, and individual circumstances. In most cases, physical therapy is a long-term approach and requires regular sessions to manage symptoms and improve mobility. It is important to work closely with a physiotherapist to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
WHAT ARE THE PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PHYSIOTHERAPY
Here are some of the physiotherapy treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) that can help manage its symptoms and improve overall physical function:
- Range of motion exercises: A physiotherapist can help develop an exercise program that includes range of motion exercises, which can help to improve joint mobility and flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises can help to improve muscle strength and reduce joint pain by providing more support to the affected joints.
- Aerobic exercises: Aerobic exercise, such as walking or cycling, can help to improve overall physical function, reduce fatigue, and increase cardiovascular health.
- Hydrotherapy: Hydrotherapy involves exercises performed in a pool, which can help to reduce joint pain and stiffness by taking pressure off the joints.
- Heat and cold therapy: Heat therapy, such as a warm towel or heating pad, can help to reduce joint stiffness and improve mobility. Cold therapy, such as an ice pack or cold towel, can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Joint protection techniques: A physiotherapist can teach you techniques to protect your joints during everyday activities, such as using assistive devices or modifying your movements.
- Assistive devices: Braces, splints, and other assistive devices can help to support affected joints and reduce pain.
WHAT ARE THE CHIROPRACTOR TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
It is important to note that chiropractic treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is controversial and not commonly used as a primary treatment option. However, here are some of the techniques a chiropractor may use to alleviate symptoms of RA:
- Spinal adjustments: Chiropractors use manual adjustments to manipulate the spine and other joints to help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Massage therapy: Soft tissue massage can help to reduce muscle tension and stiffness, which may provide some relief from joint pain.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves inserting needles into specific points on the body to help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ultrasound therapy: Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to help reduce inflammation and improve circulation to affected joints.
- Electrical stimulation: Electrical stimulation involves applying a mild electrical current to affected muscles to help reduce pain and improve muscle function.
WHAT ARE THE ACCUPRESSURE OR ACCUPUNTURIST TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Acupressure and acupuncture are traditional Chinese medicine techniques that may help reduce pain and inflammation in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Here are some of the techniques used by acupressure and acupuncture practitioners:
- Acupuncture needles: Acupuncture needles are inserted into specific points on the body to stimulate the body’s natural healing response and reduce inflammation.
- Cupping therapy: Cupping therapy involves placing cups on the skin to create suction, which can help to reduce muscle tension and pain.
- Moxibustion: Moxibustion involves burning dried herbs close to the skin to stimulate blood flow and reduce inflammation.
- Electrical stimulation: Electrical stimulation is sometimes used in conjunction with acupuncture to help stimulate the nerves and reduce pain.
- Acupressure massage: Acupressure massage involves applying pressure to specific points on the body to help reduce muscle tension and pain.
Acupuncture and acupressure may be used as complementary therapies alongside other treatments, such as medication and physiotherapy, to help manage RA symptoms.
WHAT ARE YOGA TREATMENT FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS , ALONG WITH RELEVANT YOGA ASANAS
Yoga can be a helpful adjunct treatment for managing the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Here are some yoga asanas and practices that can be beneficial:
- Warm-up poses: Start with gentle warm-up poses like Cat-Cow stretch, Neck stretch, Shoulder rolls, and gentle spinal twists to loosen up the joints and muscles.
- Joint loosening practices: Move on to joint loosening practices such as Gomukhasana (Cow face pose), Garudasana (Eagle pose), and Supta Padangusthasana (Reclining hand-to-big-toe pose) to improve joint mobility and flexibility.
- Gentle standing poses: Practice gentle standing poses like Tadasana (Mountain pose), Trikonasana (Triangle pose), and Virabhadrasana II (Warrior II pose) to improve balance, strength, and stability in the lower body.
- Seated poses: Incorporate seated poses like Paschimottanasana (Seated forward bend), Janu Sirsasana (Head-to-knee forward bend), and Baddha Konasana (Butterfly pose) to stretch and release tension in the hips, lower back, and hamstrings.
- Pranayama: Practice Pranayama or breathing techniques such as Kapalabhati, Bhastrika, and Nadi Shodhana to increase lung capacity and improve oxygen circulation.
It’s essential to work with a qualified yoga teacher or therapist who can tailor the practice to your specific needs and limitations.
WHAT DO’S AND DON’TS ADVICE IS GIVEN TO PATIENTS HAVING RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are often given specific advice on what they should and should not do in order to manage their condition and prevent further damage. Here are some general do’s and don’ts that may be recommended:
DO’S:
- Do engage in low-impact exercise such as walking, swimming or yoga to improve flexibility and maintain muscle strength.
- Do maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Do get enough rest and sleep to reduce stress and allow the body to heal.
- Do take prescribed medication and follow the recommended treatment plan to manage symptoms and slow down disease progression.
- Do use assistive devices such as splints or braces to support painful joints and reduce stress on them.
DON’TS:
- Don’t engage in high-impact activities such as running, jumping, or sports that put too much stress on the joints.
- Don’t smoke or consume alcohol as it can worsen inflammation and interfere with medication.
- Don’t ignore warning signs such as joint pain, stiffness, or swelling. Early detection and treatment can prevent further damage.
- Don’t engage in activities that involve repetitive motions that put pressure on the joints.
- Don’t push yourself too hard, listen to your body and take breaks when needed.
It’s important to note that every individual’s condition is different, and a physiotherapist will create a personalized plan that best suits the patient’s needs.
WHAT ARE THE RECOMMENDED SIMPLE STREGTHENING, SUPPORTING DEVICES OR BANDS AND EXERCISE MACHINES , BOOKS , OTHERS FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PHYSIOTHERAPY PERSON FOR EASY AND QUICK TREATMENT OR RECOVERY?
Recommended Strengthening and Supporting Devices for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Physiotherapy:
- Splints and Braces: Splints and braces can help support the affected joints and reduce pain and inflammation. They can also help improve joint stability and prevent further damage. Your physiotherapist can recommend the appropriate splint or brace for your specific needs.
- Resistance Bands: Resistance bands are a low-impact way to strengthen muscles and improve joint mobility. Your physiotherapist can recommend specific exercises using resistance bands to help improve your strength and flexibility.
- Exercise Machines: Certain exercise machines, such as stationary bikes and elliptical trainers, can be beneficial for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. They provide low-impact cardiovascular exercise and help improve joint mobility.
- Yoga Props: For individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, using props like blocks, straps, and blankets during yoga practice can help modify poses and make them more accessible. Your physiotherapist can recommend specific modifications and props to use during your yoga practice.
Recommended Books and Other Resources for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Physiotherapy:
- “The First Year: Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Essential Guide for the Newly Diagnosed” by M.E.A. McNeil
- “Arthritis: Exercise, Diet, and Alternative Therapies” by Dr. Sharon L. Kolasinski
- Arthritis Foundation (www.arthritis.org): The Arthritis Foundation offers resources and support for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, including exercise programs and educational materials.
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (www.niams.nih.gov): The NIAMS offers information on research and treatment for arthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders.
OTHER SIMILAR PHYSICAL THERAPY CONDITIONS RELATED TO RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
There are several physical therapy conditions related to rheumatoid arthritis that may benefit from physiotherapy treatment. Some of them are:
- Osteoarthritis: This is a degenerative joint disease that can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Physical therapy can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase flexibility.
- Fibromyalgia: This is a condition that causes widespread muscle pain and fatigue. Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and flexibility, reduce pain, and increase endurance.
- Ankylosing spondylitis: This is a type of arthritis that affects the spine and can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Physical therapy can help improve posture, flexibility, and range of motion in the spine.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: This is an autoimmune disease that can cause joint pain, fatigue, and skin rashes. Physical therapy can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase overall strength and endurance.
- Gout: This is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid in the joints. Physical therapy can help reduce pain, improve joint function, and increase flexibility.
In general, physical therapy can be beneficial for a variety of conditions that affect the joints, muscles, and bones.
WRITE DIET PLAN FOR VEGETARIAN, NON-VEGETARIAN AND VEGAN FOR PERSON SUFFERING FROM RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND OTHER AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS FOR QUICK RECOVERY
As a nutritionist, it is important to understand that a balanced diet can play a crucial role in managing rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disorders. Here are some dietary recommendations for individuals with these conditions:
DIET PLAN FOR VEGETARIANS:
- Include more plant-based sources of protein such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, garlic, and leafy green vegetables in the diet.
- Consume fruits like berries, apples, and oranges, which are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C.
- Limit the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates.
- Make sure to include enough calcium and vitamin D sources like dairy products, fortified plant-based milk, and leafy greens.
DIET PLAN FOR NON-VEGETARIANS:
- Consume lean sources of protein like fish, poultry, and lean cuts of meat.
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, garlic, and leafy green vegetables in the diet.
- Consume fruits like berries, apples, and oranges, which are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C.
- Limit the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates.
- Make sure to include enough calcium and vitamin D sources like dairy products and leafy greens.
DIET PLAN FOR VEGANS:
- Include more plant-based sources of protein such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, garlic, and leafy green vegetables in the diet.
- Consume fruits like berries, apples, and oranges, which are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C.
- Consume fortified plant-based milk and cereals to ensure enough calcium and vitamin D intake.
- Consider taking supplements like vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acids, which may be lacking in a vegan diet.
In general, it is important to avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of refined carbohydrates. It is also important to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
FAQ ON RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Some frequently asked questions (FAQs) and answers about Rheumatoid Arthritis in physiotherapy:
Q: What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
A: Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints. It is a chronic condition that can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints.
Q: How is Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosed in physiotherapy?
A: A physiotherapist can diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis by performing a physical exam, reviewing medical history, and ordering imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound.
Q: What are the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
A: The symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
Q: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis be treated with physiotherapy?
A: Yes, physiotherapy can help manage the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis. It can also improve joint flexibility and range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, and increase strength and endurance.
Q: What are some common physiotherapy treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis?
A: Some common physiotherapy treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis include joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, and hydrotherapy.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage Rheumatoid Arthritis?
A: Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy diet, stress management, and getting enough rest can help manage the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Q: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis be cured?
A: Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic condition that has no cure. However, with proper treatment and management, it is possible to control the symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Q: Is physiotherapy the only treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis?
A: No, there are other treatment options for Rheumatoid Arthritis including medications, injections, and surgery. A physiotherapist can work with other healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for each patient.
Q: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis cause permanent joint damage?
A: Yes, if left untreated or poorly managed, Rheumatoid Arthritis can cause permanent joint damage and deformity. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent joint damage.
Q: Can Rheumatoid Arthritis affect other parts of the body besides the joints?
A: Yes, Rheumatoid Arthritis can also affect other parts of the body including the eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
Q: What does a physiotherapist do for rheumatoid arthritis?
A: A physiotherapist can help with rheumatoid arthritis by developing an individualized exercise program to help improve joint mobility, strength, and function. They can also provide manual therapy, education on joint protection and energy conservation, and use modalities such as heat or ice to reduce pain and inflammation.
Q: What kind of physical therapy is used for rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Physical therapy for rheumatoid arthritis typically involves a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and modalities. Exercises may include range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and aerobic exercise. Manual therapy may include joint mobilization or soft tissue massage. Modalities such as heat or ice may also be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
Q: What is rheumatoid arthritis ICD 10 code?
A: The ICD-10 code for rheumatoid arthritis is M05. It includes codes for different types of rheumatoid arthritis, such as M05.0 for rheumatoid lung disease and M05.8 for other specified rheumatoid arthritis.
Q: What are the medications used to treat rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Medications used to treat rheumatoid arthritis include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents. NSAIDs are used to reduce pain and inflammation, while DMARDs and biologic agents are used to slow the progression of the disease and prevent joint damage.
Q: Is there a specific diet for rheumatoid arthritis?
A: While there is no specific diet for rheumatoid arthritis, it is recommended to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and nuts may also be beneficial for reducing inflammation.
Q: How does rheumatoid arthritis affect the hands?
A: Rheumatoid arthritis commonly affects the small joints in the hands, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and deformity. The joints may also become warm and tender to the touch.
Q: What is the difference between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis?
A: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that affects the joints, causing inflammation and damage. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease caused by wear and tear on the joints over time.
Q: What tests are used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Tests used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis include blood tests for rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, as well as imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasounds to look for joint damage.
More Articles: